Even if you’re not a cannabis expert, you’ve probably heard of cannabis derived terpenes. But what are cannabis derived terpenes and why do they matter? Do terpenes get you high? And what’s the big deal about the entourage effect? Let’s just say that when scientists started taking a close look at cannabis, they discovered some groundbreaking things about this beloved plant.
Cannabis connoisseurs of the past were mainly concerned with THC levels. However, today we know that various compounds, like terpenes, influence the overall taste, aroma, and even the effects of different chemovars. Actually, terpenes are all around us! You might be enjoying the effects of terpenes at this very moment (ever tried aromatherapy?).
That still doesn’t explain precisely what terpenes are though. Fear not. While it does involve a bit of chemistry, you don’t need a STEM degree to understand what terpenes are or how they influence your cannabis experience.
Read on and discover what cannabis derived terpenes are, the difference between synthetic terpenes and botanical terpenes, common terpenes, and so much more.
So, What Are Terpenes?
In the most basic sense, terpenes are compounds that dictate the overall flavor, aroma, and some of the effects of various plants. Have you ever enjoyed the scent of a rose? How about the sharp citrus flavor of an orange? Terpenes are largely responsible for these experiences.
Each plant produces a terpene profile (various terpenes in different ratios) that has a unique scent, taste, and effect. Lavender, for example, has a LOT of a terpene called Linalool. On top of smelling floral and herbaceous, this terpene has potent sedative qualities. That’s why lavender is so calming! But why do plants produce terpenes? How does it benefit the plants?
Plants produce these ‘volatile organic compounds’ for several reasons. While some plants use bright colors to attract pollinators, others use terpenes to attract bees and various insects. In that instance, terpenes are necessary for plant reproduction (1). In other instances, terpenes offer protection by repelling certain insects and herbivores (2). There are even times when terpenes provide sun protection (3) and protection against certain pathogens (4). That’s just the beginning! Scientists are still discovering more and more ways that terpenes benefit plants.
Bottom line? Terpenes play an important evolutionary role that allows plants to interact and respond in their environment to increase the chances of survival. Now we get to dive into the different types of terpenes and why terpenes are essential to your cannabis experiences.
Synthetic Terpenes vs Botanical Terpenes
Technically, people have been using terpenes in their products for a LONG time. Anytime someone manufactures a product using plant matter, some of the terpenes end up in the finished product. The problem is that terpenes are volatile.
That means they’re incredibly sensitive to things like heat, rough handling, and even weather. So, two seeds from the same plant might end up having different terpene profiles. Things like farming practices and soil quality can influence the ways terpenes are expressed. It also means that manufacturing processes often destroy most of the natural terpenes in plant matter. That’s why so many people simply add synthetic and/or botanical terpenes to their products.
Botanical terpenes are any terpenes extracted directly from a plant source (cannabis derived terpenes get their own category though). Synthetic terpenes are produced in a lab by chemical blending and manipulation. Both types of terpenes are important for several reasons.
Relying on JUST plant matter to flavor your products can be incredibly time-consuming and expensive. You would have to source plants from a farming operation that ensures consistency in terpene expression (which is difficult), plus you would have to use LOTS of plant matter in the hope that enough terpenes would survive the manufacturing process. So synthetic and botanical terpenes save people a lot of time and money. The issue is that not all synthetic and botanical terpenes are intended for vaping.
Some isolates, like D-limonene, have been shown to irritate the respiratory pathway when used in high concentrations. While that might also be true of cannabis derived limonene, both synthetic and botanical terpenes are more likely to have impurities. Additionally, some botanical terpenes are used as viscosity agents (also known as thickening agents). Most vape cartridges use a viscosity agent and while some may be safe, others have been shown to produce toxic byproducts when heated. In the case of cartridges, botanical terpenes have been used to replace Vitamin E Acetate, MCT Oil, and more…but that doesn’t guarantee they’re any safer. In fact, terpenes like squalane and squalane or phytol that have seen widespread use as viscosity agents and may be even worse (12)(13).
In the end, it really depends on the extraction method and plant sources when it comes to terpenes. To be safe, always do your research when trying new products. If you can, find out where the terpenes come from and try to stick with terpene companies that follow NCIA Safe Vaping Regulations (5).
What Are Cannabis Derived Terpenes?
Cannabis derived terpenes are simply any terpenes extracted from the cannabis plant. That’s right. Technically, they’re the same terpenes you can find in botanical sources (D-limonene, myrcene, beta-caryophyllene, etc.). However, for legal reasons, terpenes extracted from cannabis get their own category.
While botanical and synthetic terpenes are legal almost everywhere, cannabis derived terpenes are only legal in certain states with legalized cannabis. Even then, they’re often difficult to ship due to the mountain of red tape that goes along with them. This makes extracting terpenes from cannabis very expensive and sometimes inefficient. However, there’s a lot to be said for products that mimic specific cannabis chemovars as closely as possible.
In addition to the potentially greater unknown risk in consuming synthetic or botanical terpenes, products with cannabis derived terpenes tend to come from higher quality small-batch operations. That’s because the increased cost and difficulty of obtaining cannabis derived terpenes doesn’t scale so well into high-volume production. It’s easier to keep things ‘in-house’ among cannabis growers and processors themselves, which is the essence of a ‘craft’ product. Furthermore, pairing cheap distillate with expensive terpenes isn’t logical, so the use of cannabis derived terpenes may be a clue that the manufacturer has also sourced their cannabinoids carefully, or even from the same ‘single source’ as the terpenes.
The Important Compounds of a Cannabis Plant
If you’ve sampled both THC isolates and products with the full-spectrum of cannabis compounds, you’ll know they provide drastically different experiences. That’s because all of the compounds in cannabis play an important role when it comes to how each strain will affect you.
Trichomes
If you’ve ever admired the sparkling, sticky crystal-like coating on a cannabis bud, you’ve looked at its trichomes. These resin glands consist of a stalk that holds up the round head. The head, however, is where you’ll find all sorts of goodies (terpenes, cannabinoids, etc.)
Cannabinoids
These are the chemical compounds that, when ingested, interact with our natural endocannabinoid systems. Some cannabinoids are psychoactive while others are anti-inflammatory, anxiolytic, etc. There are over one hundred different cannabinoids and they’re found plentifully in cannabis, but also in other botanical sources as well.
THC
THC, delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol, or Δ-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ-9-THC) is the main psychoactive cannabinoid found in the cannabis plant.
CBD
CBD, or cannabidiol, is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid found in the cannabis plant. It doesn’t directly bind to the CB1 or CB2 receptors in the same way that THC does, but many find that it helps relieve anxiety, inflammation, insomnia, etc.
Terpenes
These ‘volatile organic compounds’ are aromatic compounds produced by most plants. They are the primary component of plant essential oils and are found in large amounts in cannabis. They influence the aroma, flavor, and effects of each cannabis chemovar.
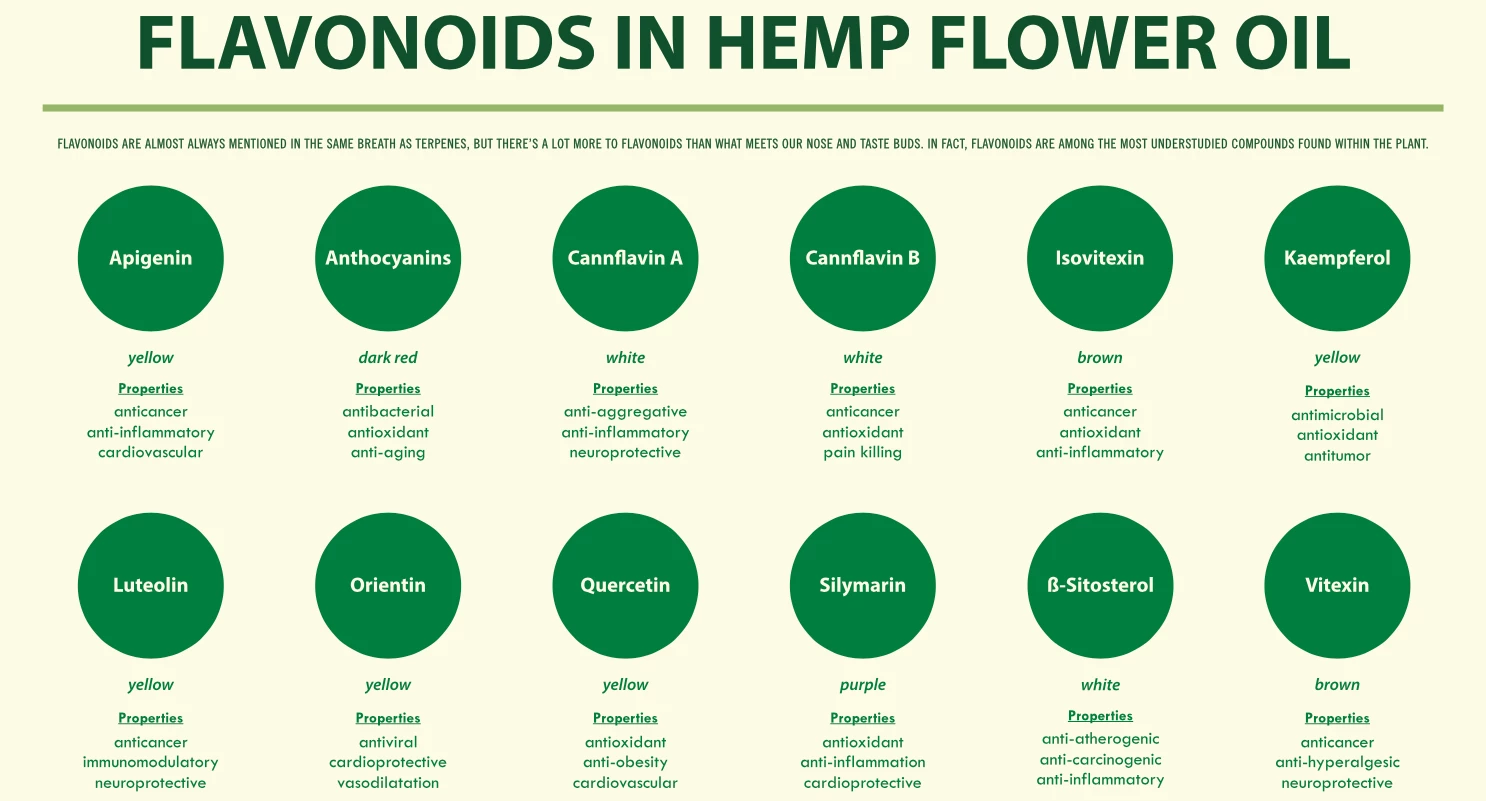
Flavonoids
Similar to terpenes, flavonoids influence the taste and smell of plants. Additionally, they can influence color, are potent antioxidants, and may influence the medicinal benefits of cannabis (6). The most recognizable flavonoid in cannabis is probably anthocyanin which is responsible for purple pigmentation and the classic ‘purp’ flavor.
The Most Common Terpenes Found in a Cannabis Plant
We’ve talked a lot about cannabis derived terpenes, but we haven’t yet talked about the specific terpene isolates you can find in the cannabis plant. While this isn’t an exhaustive list, here are a few of the most common terpenes found in the cannabis plant, what they smell like, what botanical sources also contain these isolates, and some of their therapeutic benefits.
Myrcene
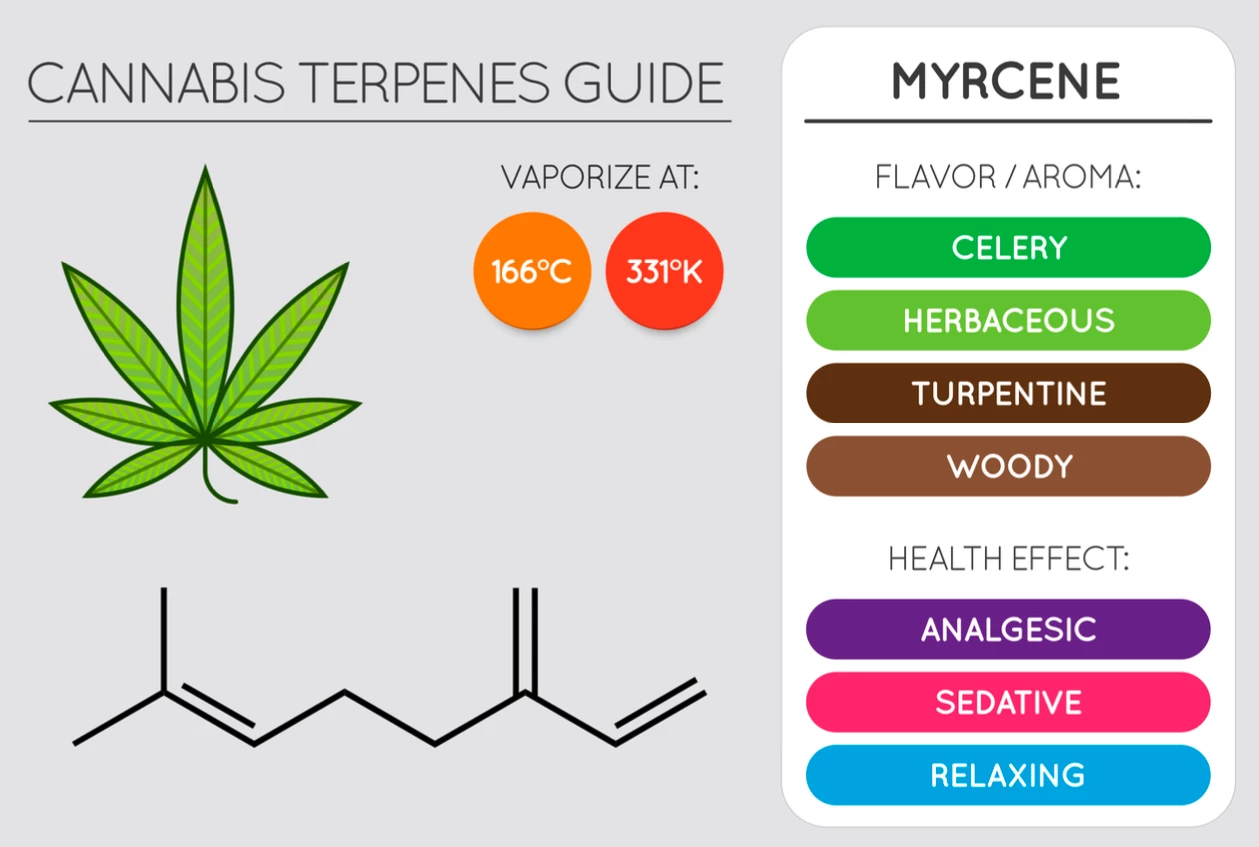
Found commonly in mangoes, bay, cardamom, parsley, and hops, Myrcene has a clove-like scent with notes of earth, pepper, mint, and fruit. This isolate has sedative, anxiolytic, anti-inflammatory, and analgesic properties (7).
Limonene
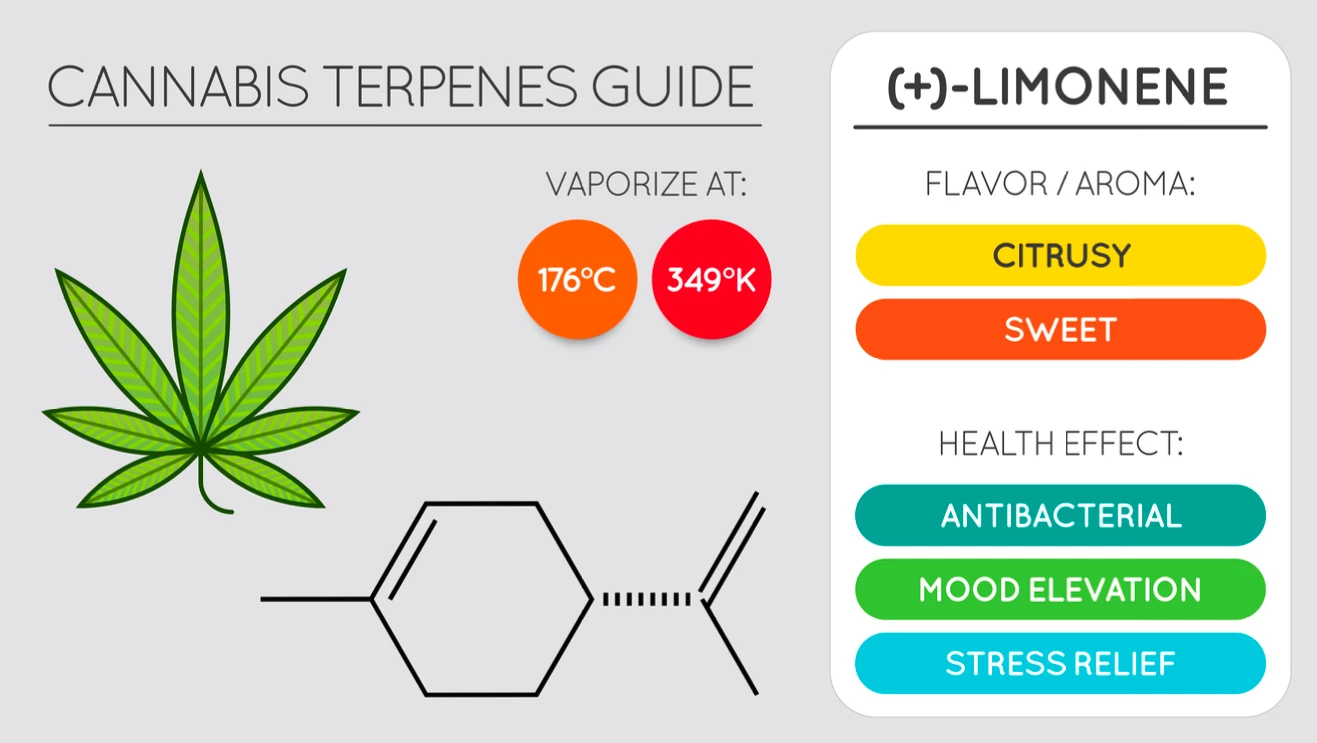
Unsurprisingly, Limonene is commonly found in lemons and other citrus fruits like limes, oranges, and grapefruits. It has a distinctly sweet, citrusy smell and studies have shown it to have anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antinociceptive, anticancer, antidiabetic, antiviral, and gastroprotective properties (8).
Pinene
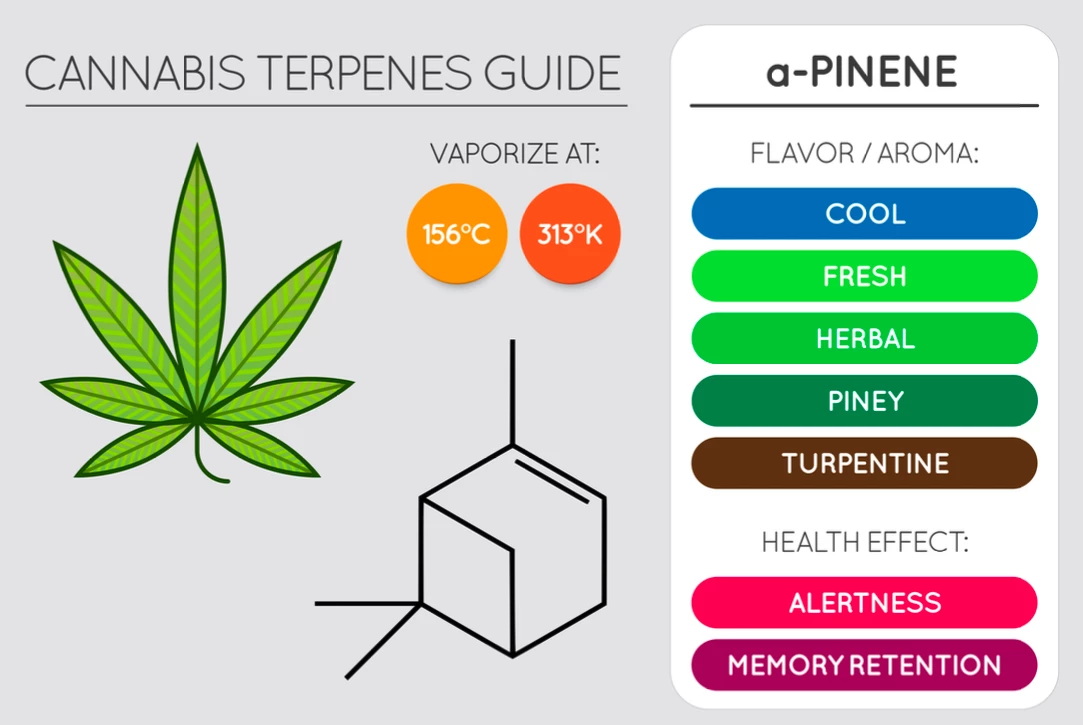
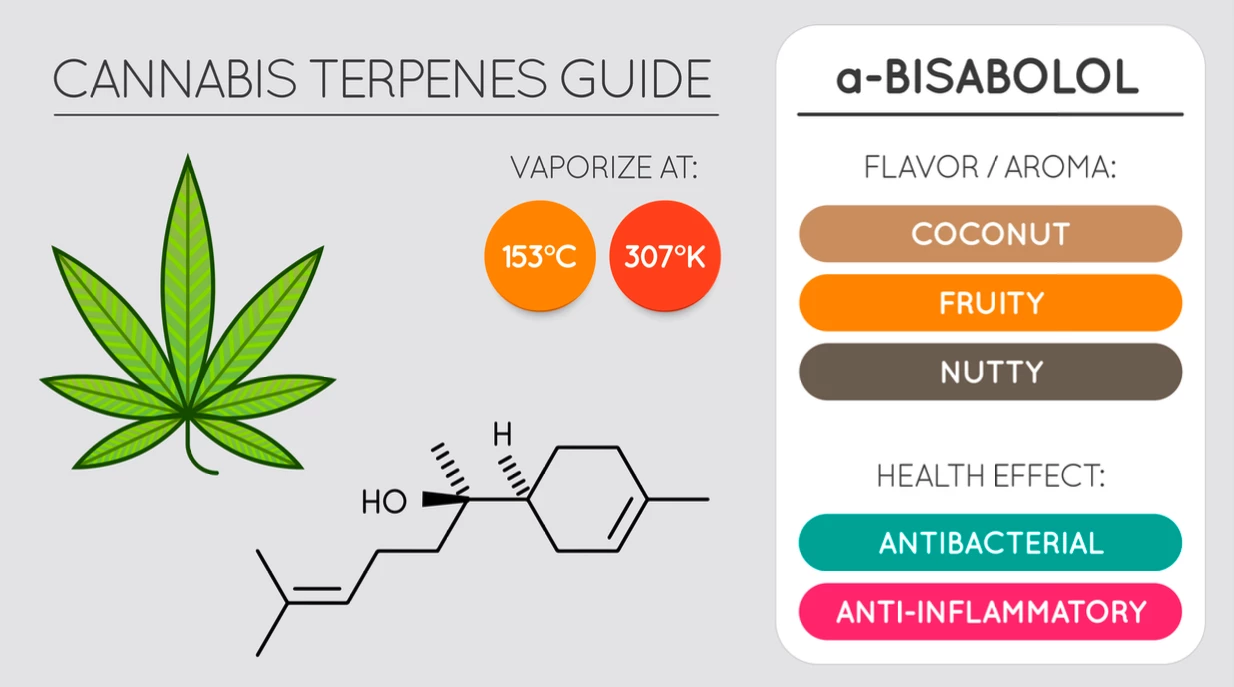
Both alpha-pinene and beta-pinene are commonly found in conifer trees and herbs like rosemary. Both have the camphoraceous scent of pine and have gastroprotective, anxiolytic, cytoprotective, anticonvulsant, and neuroprotective properties (9).
How Terpenes Benefit/Affect Your High
You may have gathered this by now, but terpenes have a big influence on your actual high. Think of it this way. Psychoactive cannabinoids like THC get you high. They’re like an elevator that goes up and down. Terpenes, however, actually take you somewhere. For example, two different chemovars with the exact same amount of THC can give you a wildly different high. That’s because of terpenes!
That’s why some strains give you couch-lock while others make you want to clean your entire house. But there’s more to it than that.
Are Terpenes Responsible for Getting You High?
Terpenes, on their own, are not psychoactive drugs. So, no, terpenes are not responsible for getting you high. They do have a strong influence on mood, however, and therefore terpenes can greatly alter the type of high you’ll have.
Have You Heard of the ‘Entourage Effect?’
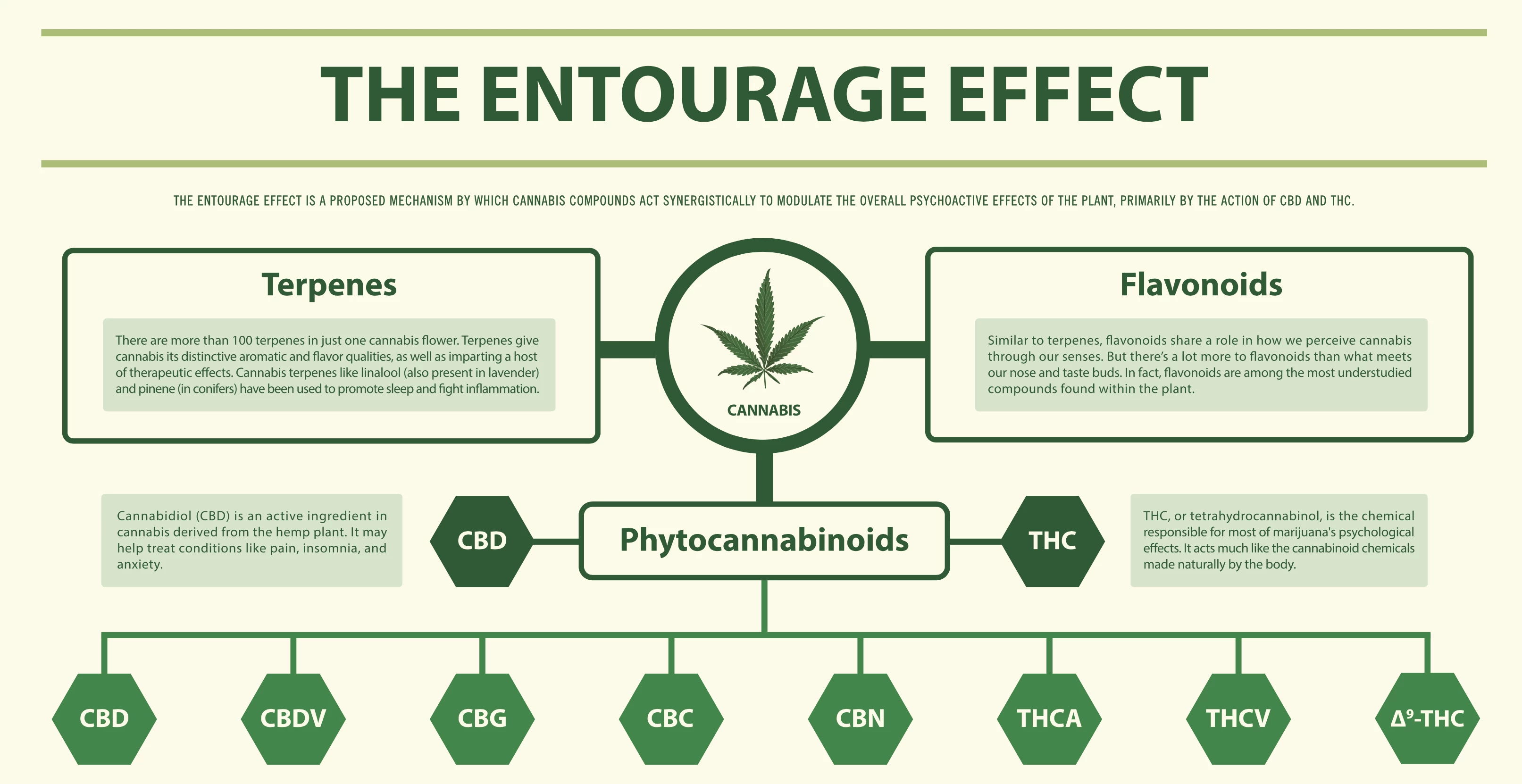
The Entourage Effect is the theory that all the various compounds in the cannabis plant work synergistically together to have a greater effect than they’re capable of on their own (10). One of the best analogies comes from prominent cannabis researcher Dr. Ethan Russo who said, “2 + 2, instead of equaling 4, it gives you an 8 in terms of the benefit” (11).
Originally, this theory was introduced by Dr. Ethan Russo as a way to get pharmaceutical approval for Epidiolex (a combination of THC and CBD for pediatric epilepsy). At the time, a phenomenon like that was fairly unprecedented and there’s still a lot of research needed to demonstrate how terpenes may or may not modulate the effects of cannabinoids.
One way to think about it is like having a beer or coffee with a joint. While adding these compounds definitely changes the high, it’s not necessarily because they affect THC. It could just be because beer and coffee provide overlapping effects that influence the overall experience.
What is a Terpene Profile?
A terpene profile is the combination of various terpene isolates. Each chemovar has a unique terpene profile, which is why they have unique flavors, aromas, and effects. A terpene chart will show you the specific ratios of terpene isolates.
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2718223/
- https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/21/19/7382/htm
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0031942213003336?via%3Dihub
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6651100/
- https://thecannabisindustry.org/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33681553/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8326332/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29427589/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6920849/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3165946/
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=C-UwA2O6gA4
- https://www.oregon.gov/olcc/Docs/commission_agendas/2020/Presentation-Squalene-and-Squalane-as-Adulterants.pdf
- https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/08958378.2020.1867260?journalCode=iiht20
